Purdue ELLLPS
Language Assessment Tools
The language assessment tools provided for use on the Purdue English Language Learners (ELL) Language Portraits (Purdue ELLLPs) are proven formative assessments that effective teachers use to determine their ELL students’ current level of ability, to understand their strengths, to identity areas in need of improvement, and to plan future instruction that will build upon and address these strengths and needs.

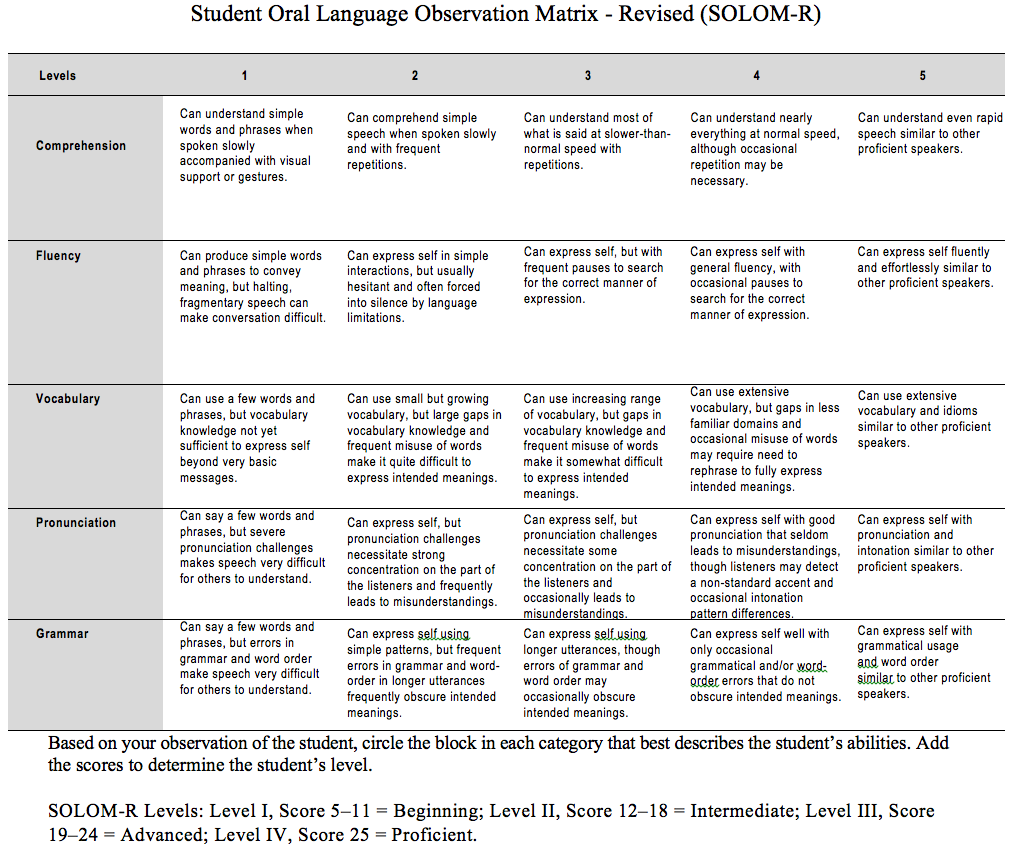
Student Oral Language Observation Matrix – Revised (SOLOM-R)
Overview
The Student Oral Language Observation Matrix (SOLOM) was first developed in the 1980s by bilingual teachers in California as a formative assessment to quickly gauge the listening and speaking ability of English language learners in English (and also the Spanish listening and speaking skills of English-proficient students in dual language bilingual education programs).
The SOLOM was revised by Wright in his book Foundations for Teaching English Language Learners: Research, Theory, Policy, and Practice (Brookes Publishing). (See Figure 1).
Five Aspects of Oral Language
The Student Oral Language Observation Matrix-Revised (SOLOM-R) emphasizes what ELLs can do at each level of English proficiency and brings the original SOLOM up to date with current research on oral language development. The SOLOM-R helps teachers focus on five aspects of oral language:
- Comprehension – Engage the student in an informal or formal oral language tasks (e.g., conversations, interactive pair or group work, oral presentation, story retelling, or other performance requiring listening and speaking)
- Fluency – How well does the student speak? Are you able to have a conversation with him or her? Does the student’s speech flow well but occasionally gets stuck as he or she searches for the correct word?
- Vocabulary – How well does the student speak? Are you able to have a conversation with him or her? Does the student’s speech flow well but occasionally gets stuck as he or she searches for the correct word?
- Pronunciation – Are others able to understand what the student is saying? Do accent or intonation patterns sometimes lead to miscommunication?
- Grammar – Are grammar errors so frequent it is hard to understand the student? Or do they only occasionally obscure the meaning he or she is trying to convey?
Source: Wright (2025, p. 205)
Instructions for Administration and Evaluation of the SOLOM-R
- Engage the student in an informal or formal oral language tasks (e.g., conversations, interactive pair or group work, oral presentation, story retelling, or other performance requiring listening and speaking)
- Scores the students in each of the five areas above on a scale of 1 to 5.
- Add the scores to determine the student’s overall evaluation of the student’s oral language proficiency. The higher the score, the higher the student’s level of proficiency.
- Identify the student’s strengths, areas in need of improvement, and instructional activities that would benefit the student’s oral language development.
For the Purdue ELL Portraits, video clips of student interviews and oral presentations are provided along with blank SOLOM-R forms.
Running Records
Overview
A running record is a tool for in-depth observation and analysis of a student’s reading performance. It is essentially a visual recording of the student’s reading word by word. It enables a teacher to identify the reading strategies the student may or may not be using and the types of errors the student makes while reading. It provides teachers with valuable formative assessment data on students’ foundational reading skills, as emphasized under the “Science of Reading” (SOR), including phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and reading comprehension when reading actual extended texts.
As Wright (2025) explains, “These errors suggest what may be going on in the students’ mind as he or she attempts to decode words and make meaning from the text. Running records allow a teacher to quickly assess the students’ strengths and areas in need of improvement” (p. 245). An example of completed Running Record is provided in Figure 2.
Instructions for Administration and Evaluation of a Running Record
- Select a text you believe is at the student’s instructional level
- Prepare a running record form with a selection of text (no more than 100 words)
- As the student reads the text from the original source (e.g., a picture book), record their reading using the following markings
- Correct Reading – Write a check mark ✓ above each word read correctly
- Omission Error – Write a dash (—) above each word that was omitted (skipped) without any effort to read it
- Substitution Error – Write the incorrect word the student said above the word the student read incorrectly
- Insertion Error – Write an insertion mark (^) at the point of insertion and write the inserted word
- Told Word Error (T) – If a student gets stuck on a word and appeals or help, or won’t go on, tell the student the correct word. Write a T and circle the T above the word to indicate “told.”
- Try That Again (TTA) Error – if a students reads a sentence or long phrase with several errors, and you think the student is capable of reading more accurately, you can ask the student to “Try that again.” Write TTA above the end of the sentence or phrase. Previous errors are discarded, but a TTA counts as 1 error (even if the student re-reads the sentence/phrase correctly)
- Repetition – Write the letter R at the point of repetition and draw a line back to the beginning of the repeated text. Add tally marks as after the R to indicate the number of times the text was repeated. Repetition does not count as an error.
- Self Corrections – If a student corrects an omission, insertion, or substitution error on his or her own, disregard the error and write (SC) above the point of self-correction
- Long Pause – If the student makes a long pause before reading a word, write a double forward slash // before the word. Pauses do not count as an error.
- Decoding attempts – If a student is audibly sounding out parts of the word as they attempt to decode, you may record these attempts above the word (e.g., sssss | aaaa | t |) Write a check mark if the student successfully reads the word (e.g., “sat”). Decoding attempts do not count as an error if the student is able to ultimately read the word correctly.
- On the running record sheet, keep a tally of the number of errors and self-corrections per line.
- Add up the total number of errors.
- Determine the number of words read correctly by subtracting the number of errors from the total number of words.
- Calculate the percentage of words read correctly by dividing the number of words read correctly by the total number of words.
- Determine the level of difficulty of the text by using the percentage of words read correctly
- 95% + = Easy
- 90% – 94% = Instructional
- Less than 90% = Frustration
- Ask the student comprehension questions about the text and write down their answers.
- Identify the students strengths, areas in need of improvement, and instructional activities that would benefit the student’ reading development.
For the Purdue ELL Portraits, video clips are provided of students reading selected texts, along with pre-prepared Running Record forms, and students’ responses to comprehension questions.
Writing Evaluations
Overview
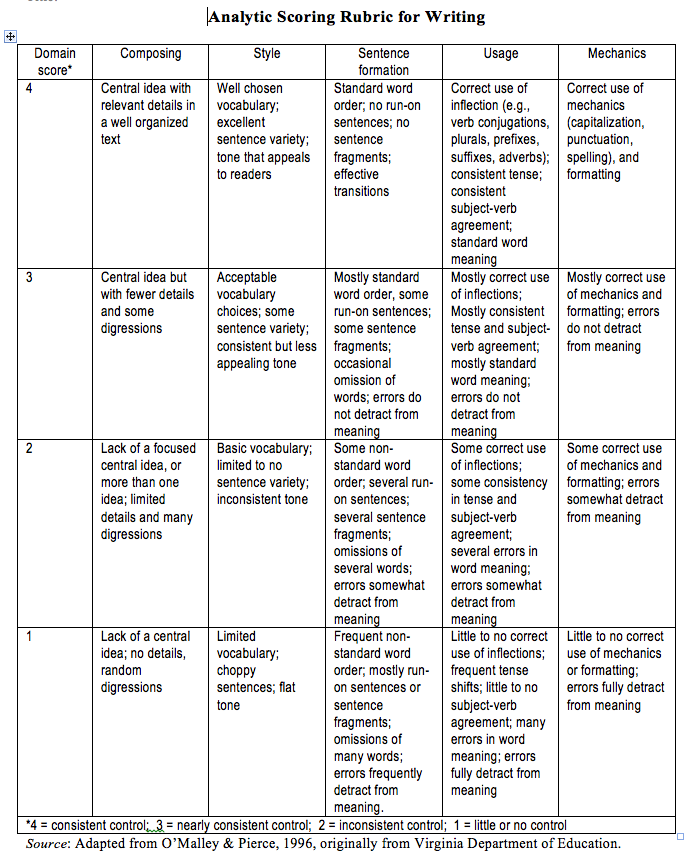
Student writing may be evaluated with a rubric designed to help teachers focus on different aspects of the student’s writing. The Analytic Scoring Rubric for Writing used on this site (see Figure 3) was first developed by educators in Virginia in the 1990s and was adapted by Wright in his book Foundation for Teaching English Language Learners: Research, Theory, Policy, and Practice (Brookes Publishing).
The rubric focuses on five areas:
- Composing – Does the text have a central idea and relevant details. Is the text well-organized?
- Style – Does the text have well-chosen vocabulary, good sentence variety, and an appealing tone?
- Sentence Formation – Are the sentences well formed with standard word order and effective transitions? Is the text free of sentence fragments and run-on sentences?
- Usage – Is there correct use of inflections (e.g., verb conjugations, plurals, prefixes, suffixes, adverbs, etc.), consistent use of tense, subject-verb agreement, and standard word meaning?
- Mechanics – Is there correct usage of capitalization, punctuation, spelling, and formatting?
Instructions for Administration and Evaluation of the Analytic Scoring Rubric for Writing
- Have students complete a piece of writing appropriate to their grade and English-proficiency level
- Read the completed writing sample and score it in each of the 5 areas of the rubric on a scale of 1 – 4.
- Identify the students strengths, areas in need of improvement, and instructional activities that would benefit the student’ written language development.
- For the Purdue ELL Portraits, writing samples are provided of students’ unedited writing, along with blank Analytic Scoring Rubric for Writing Forms.
For the Purdue ELL Portraits, writing samples are provided of students’ unedited writing, along with blank Analytic Scoring Rubric for Writing Forms.
Source: Wright, W. E. (2025). Foundations for teaching English language learners: Research, theory, policy, and practice (4th ed). Brookes Publishing.
Contact Us